With the increasing application of iodinated contrast agents in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, the adverse reactions and risks caused by iodinated contrast agents have attracted much attention.
1. Injury of acute kidney induced by iodinated contrast agents
The use of iodinated radiocontrast dye can cause an injury called contrast induced acute kidney injury (CIAKI), especially in patients with impaired renal function, patients with endothelial insufficiency, diabetic patients, and patients with insufficient hydration, who are at an increased risk.
CIAKI is only a transient injury in most patients. However, CIAKI may also cause serious consequences: patients with CIAKI have an increased probability of in-hospital complications, including death, and are likely to cause long-term renal insufficiency.
Method of prevention and treatment:
Interventional cardiovascular physicians should pay attention to the following issues when using iodinated contrast agents to reduce the damage of the contrast agents to the patient's kidneys:
(1) Fully assess the patient's risk/benefit ratio before surgery.
(2) Carry out sufficient hydration according to the individual conditions of the patient.
(3) CIAKI is a dose-dependent non-specific adverse reaction based on the patient's basic renal function and overall clinical conditions, and the smallest dose of iodinated contrast agent should be used on the premise that the conditions of imaging and diagnosis are met.
(4) Choose hypotonic or isotonic contrast agents.
2. Allergic reactions to iodinated contrast agents
According to the iohexol package insert, the common adverse reaction to iohexol contrast is skin reaction, mostly acute attack. Mild acute allergic reactions may only manifest as localized urticaria and pruritus. In severe cases, diffuse facial and laryngeal edema, bronchospasm and dyspnea, anaphylactic shock or even respiratory and cardiac arrest may occur. Inappropriate treatment will lead to permanent illness or even death.
Almost all life-threatening adverse reactions of iodinated contrast agents occur within 20 minutes after the injection of the contrast agent. Delayed allergic-like reactions are mostly common skin reactions, most of which occur within 3h to 2d after the injection.
Method of prevention and treatment:
Before using iodinated contrast agents, patients should be selected and prepared according to the general principles of using iodinated contrast agents. The iodinated contrast agent should be fully hydrated and heated to 37°C for use. If the patient has a history of allergy to iodinated contrast agents, non-ionic contrast agents with a different composition should be considered.
Make sure that the room should be equipped with first aid equipment and first aid drugs on a regular basis. Medical staff should be familiar with how to treat and rescue patients, and activate the emergency system when necessary, and promptly seek help from relevant departments.
Most of the adverse reactions to non ionic contrast agents are mild and non-life-threatening, which only require observation to dispel the doubts of the patient and symptomatic treatment. Severe and life-threatening adverse reactions are rare and unpredictable. Once an adverse reaction occurs, it is necessary to immediately stop the injection of iodinated contrast agent, and quickly assess the patient's condition and the severity of the adverse reaction, so as to adopt different treatments and measures. Although severe allergic reactions develop rapidly and are dangerous, patients rarely lose their lives if they can be treated in a timely and effective manner.
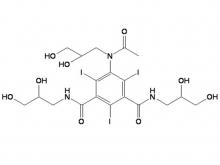
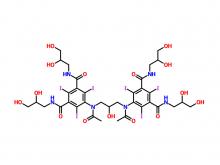
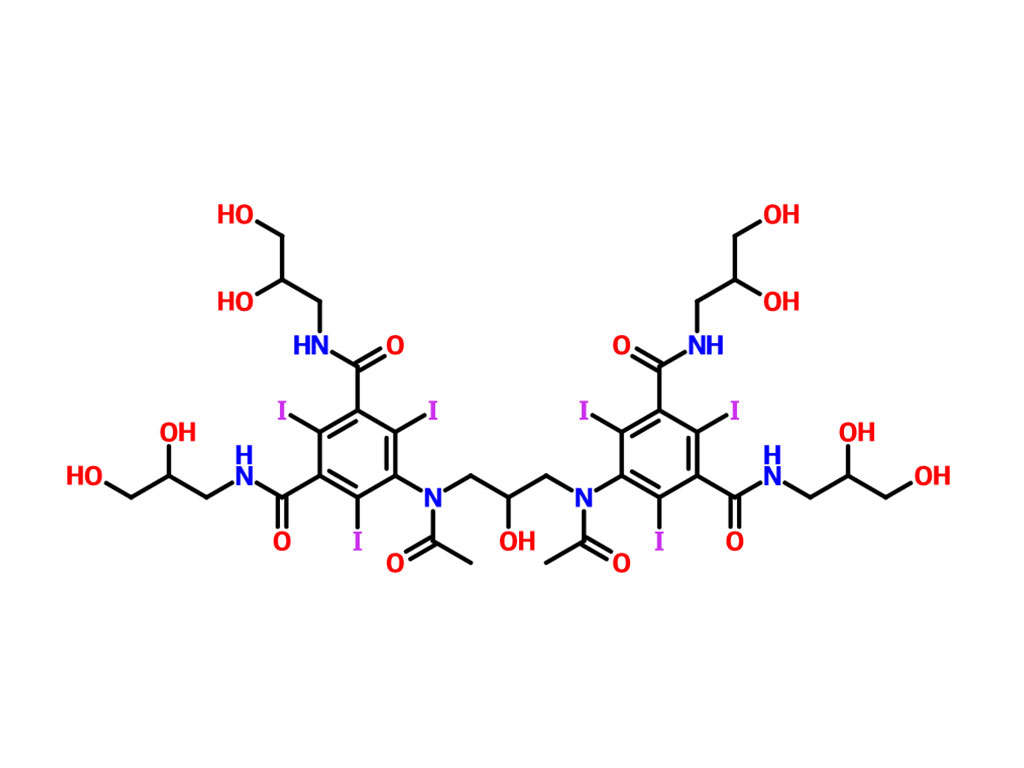
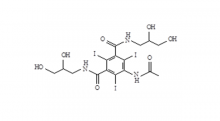 Iohexol Intermediate 5-Amino-N,N'-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide
Iohexol Intermediate 5-Amino-N,N'-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide
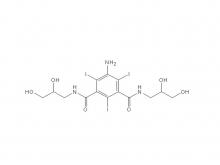 Iohexol/Ioversol Intermediate 5-Amino-N, N'-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide
Iohexol/Ioversol Intermediate 5-Amino-N, N'-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide
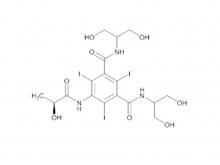
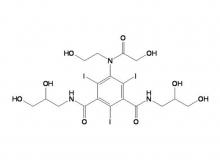
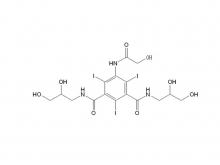 Ioversol Intermediate (order based) N, N'-Bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-(glycoloylamino)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide
Ioversol Intermediate (order based) N, N'-Bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-(glycoloylamino)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide
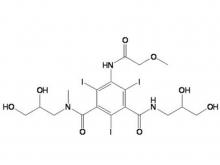
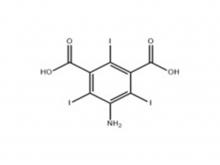 Iopamidol Intermediate (order based) 5-Amino-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalic acid
Iopamidol Intermediate (order based) 5-Amino-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalic acid
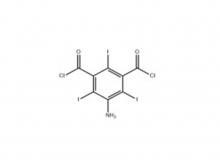 Iopamidol Intermediate (order based) 5-Amino-2,4,6- triiodisophthaloyl acid dichloride
Iopamidol Intermediate (order based) 5-Amino-2,4,6- triiodisophthaloyl acid dichloride
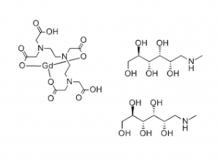
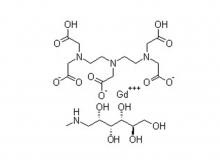
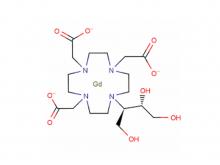
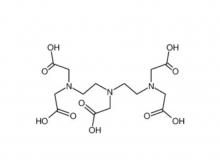 Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA)
Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA)

 EN
EN
 jp
jp  fr
fr  de
de  es
es  ru
ru  ar
ar 






 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.3 Shuiyuan West Road, Miyun District, Beijing, China
No.3 Shuiyuan West Road, Miyun District, Beijing, China 